Nose Lift Using Botox (Non-Surgical Rhinoplasty for Nose Tip Reshaping)
A nose tip lift using Botox injections is a non-surgical procedure that can slightly elevate the tip of the nose by relaxing specific muscles that cause downward pull.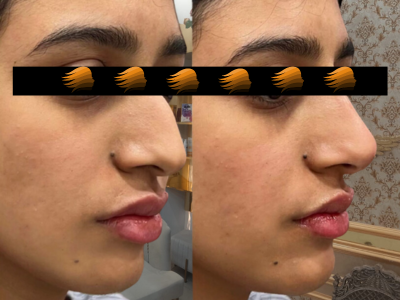
How it's Done?
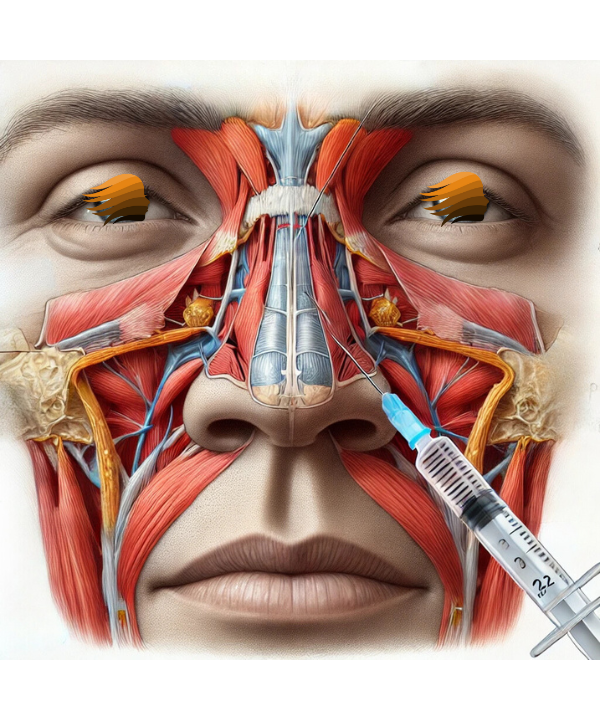
Target Muscle
The depressor septi nasi muscle is located closer to the base of the nose, just above the upper lip. It originates from the maxilla (upper jaw bone) near the incisors and inserts into the nasal septum and nostrils, pulling the tip of the nose downward when you smile or make certain facial expressions.Botox Injection: A small amount of Botox is injected into this muscle. By temporarily paralyzing or relaxing it, the downward pull is reduced, allowing the tip of the nose to lift slightly by two methods, tip rotation, correcting the angle of the nose tip and tip projection, adjusting how far the tip extends.
The nose tip plays a crucial role in both the aesthetic balance of the face and the functionality of the nose. Its appearance, structure, and position can significantly affect a person's overall facial harmony, while its functional elements influence breathing and airflow. Understanding the anatomy and various aesthetic treatments associated with the nose tip can help address both cosmetic concerns and medical conditions.
Botox Nose Tip Lift Can Address
Droopy Nose Tip
A downward-pointing nose tip can make the nose appear longer and less balanced with the rest of the face. This can be caused by overactive muscles like the depressor septi nasi, aging, or the natural shape of the cartilage.
Bulbous Nose Tip
This nose tip is characterized by excessive roundness or width, often caused by large alar cartilages or thick skin.
Nasal Tip Projection
This refers to how far the nose tip extends away from the face. Under-projection can make the nose appear flat, while over-projection can create a pinocchio effect.
Asymmetry
A crooked or asymmetrical nose tip can throw off the balance of the face. This may result from a deviation in the nasal septum, trauma, or natural development.
